Print as PDF
KEY POINTS
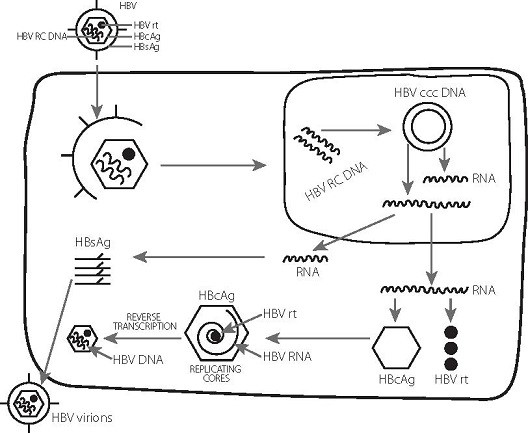
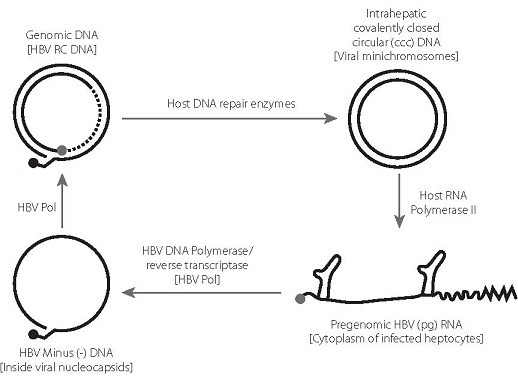
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) can cause persistent infection by the establishment of a viral covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), which forms a stable minichromosome in the hepatocyte nucleus.
- In chronic hepatitis B, the cccDNA is largely refractory to elimination by the immune response or by nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA) therapy. Upon immunosuppression or cessation of therapy, the cccDNA can re-initiate virus replication, leading to reactivation of disease.
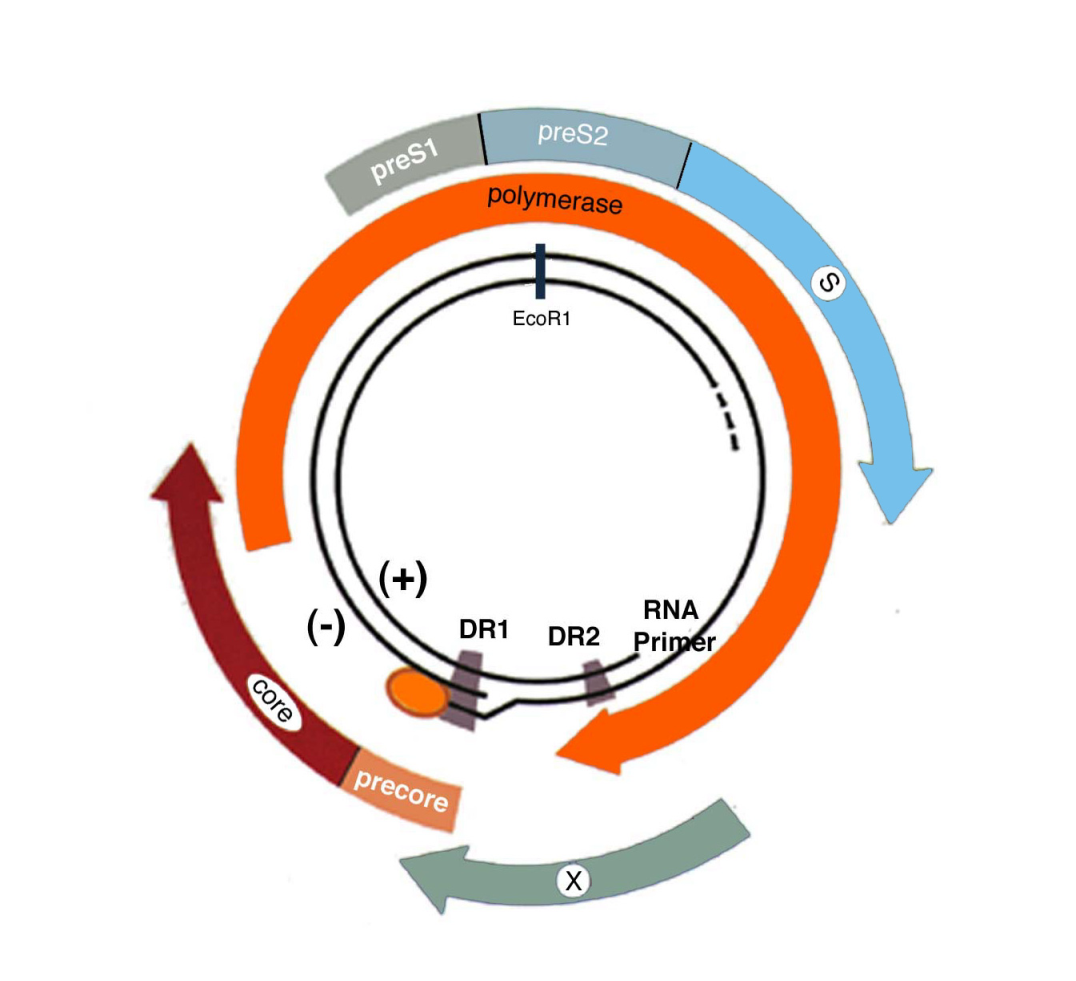
- HBV has an unusual replication strategy; it employs an error-prone reverse transcription step that allows mutations to be generated. Recent research efforts have identified several new targets for therapeutic intervention which may lead to a functional cure.
- HBV genotypes A-D are found worldwide; genotypes B and C are the major forms in Oceania and Asia. Different genotypes are associated with different rates of disease progression and risk of HCC (1).
- Lin CL, Kao JH. The clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotype: recent advances. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26 Suppl 1:123-30.
- Chisari F, Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Ann Rev Immunol 1995;13:29-60.
- Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z, et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 2012;1:e00049.
- Bock CT, Schranz P, Schroder CH, Zentgraf H. Hepatitis B virus genome is organized into nucleosomes in the nucleus of the infected cell. Virus Genes 1994;8:215-29.
- Newbold JE, , Xin H, Tencza M, Sherman G, Dean J, Bowden S, et al. The covalently closed duplex form of the hepadnavirus genome exists in situ as a heterogeneous population of viral minochromosomes. J Virol 1995;69:3350-7.
- Kramvis A. Genotypes and genetic variability of hepatitis B virus. Intervirology 2014;57:141-50.
- Milich DR, Jones JE, Hughes JL, Price J, Raney AK, McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990;87:6599-603.
- Hunt CM, McGill JM, Allen MI, Condreay LD. Clinical relevance of hepatitis B viral mutations. Hepatology 2000;31:1037-44.
- Lok AS, Akarca U, Greene S. Mutations in the pre-core region of hepatitis B virus serve to enhance the stability of the secondary structure of the pre-genome encapsidation signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994;91:4077-81.
- Bartholomeusz A, Schaefer S. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: comparison of genotyping methods. Rev Med Virol 2004;14:3-16.
- Carman WF, Zanetti AR, Karayiannis P, Waters J, Manzillo G, Tanzi E, et al. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet 1990;336:325-9.
- Carman WF, Trautwein C, van Deursen FJ, Colman K, Dornan E, McIntyre G, et al. Hepatitis B virus envelope variation after transplantation with and without hepatitis B immune globulin prophylaxis. Hepatology 1996;24:489-93.
- Shaw T, Locarnini S. Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2004;2:853-71.
- Lai CL, Dienstag J, Schiff E, Leung NW, Atkins M, Hunt C, et al. Prevalence and clinical correlates of YMDD variants during lamivudine therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis 2003;36:687-96.
- Matthews GV, Bartholomeusz A, Locarnini S, Ayres A, Sasaduesz J, Seaberg E, et al. Characteristics of drug resistant HBV in an international collaborative study of HIV-HBV-infected individuals on extended lamivudine therapy. AIDS 2006;20:863-70.
- Leung N. Clinical experience with lamivudine. Semin Liver Dis 2002;22 Suppl 1:15-21.
- Ayres A, Yuen L, Jackson KM, Manoharan S, Glass A, Maley M, et al. Short duration of lamivudine for prevention of HBV transmission in pregnancy: lack of potency and selection of resistance mutations. J Viral Hepat 2014; 21:809-17.
- Stuyver LJ, Locarnini SA, Lok A, Richman DD, Carman WF, Dienstag JL, et al. Nomenclature for antiviral-resistant human hepatitis B virus mutations in the polymerase region. Hepatology 2001;33:751-7.
- Delaney WE 4th, Locarnini S, Shaw T. Resistance of hepatitis B virus to antiviral drugs: current aspects and directions for future investigation. Antivir Chem Chemother 2001;12:1-35.
- Angus P, Vaughan R, Xiong S, Yang H, Delaney W, Gibbs C, et al. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil therapy associated with development of a novel mutation in the HBV polymerase. Gastroenterol 2003;125:292-7.
- Tenney DJ, Levine SM, Rose RE, Walsh AW, Weinheimer SP, Discotto L, et al. Clinical emergence of entecavir-resistant hepatitis B virus requires additional substitutions in virus already resistant to Lamivudine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004;48:3498-507.
- van Bommel F, de Man RA, Wedemeyer H, Deterding K, Petersen J, Buggisch P, et al. Long-term efficacy of tenofovir monotherapy for hepatitis B virus-monoinfected patients after failure of nucleoside/nucleotide analogues. Hepatology 2010;51:73-80.
- Yim HJ, Hussain M, Liu Y, Wong SN, Fung SK, Lok AS. Evolution of multi-drug resistant hepatitis B virus during sequential therapy. Hepatology 2006;44:703-12.
- Shafer RW, Winters MA, Palmer S, Merigan TC. Multiple concurrent reverse transcriptase and protease mutations and multidrug resistance of HIV-1 isolates from heavily treated patients. Ann Intern Med 1998;128:906-11.
- Natsuizaka M, Hige S, Ono Y, Ogawa K, Nakanishi M, Chuma M, et al. Long-term follow-up of chronic hepatitis B after the emergence of mutations in the hepatitis B virus polymerase region. J Viral Hepat 2005;12:154-9.
- Delaney WE 4th, Yang H, Westland CE, Das K, Arnold E, Gibbs CS, et al. The hepatitis B virus polymerase mutation rtV173L is selected during lamivudine therapy and enhances viral replication in vitro. J Virol 2003;77:11833-41.
- Chen RY, Bowden S, Desmond PV, Dean J, Locarnini SA. Effects of interferon alpha therapy on the catalytic domains of the polymerase gene and basal core promoter, precore and core regions of hepatitis B virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003;18:630-7.
- Moucari R, Mackiewicz V, Lada O, Ripault MP, Castelnau C, Martinot-Peignoux M, et al. Early serum HBsAg drop: a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients. Hepatology 2009;49:1151-7.
- Urban S, Bartenschlager R, Kubitz R, Zoulim F. Strategies to inhibit entry of HBV and HDV into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014;147:48-64.
- Seeger C, Sohn JA. Targeting hepatitis B virus with CRISPR/Cas9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2014;3:e216.
- Bourne C, Lee S, Venkataiah B, Lee A, Korba B, Finn MG, et al. Small-molecule effectors of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly give insight into virus life cycle. J Virol 2008;82:10262-70.
- Richman DD. The impact of drug resistance on the effectiveness of chemotherapy for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2000;32:866-7.